Information Interface Design Requirements
Designing the information interface refers to modalities (e.g. visual, auditory, haptic), objects (e.g. text, graphic, list, display) and may be passive or active (e.g. label, control, feedback). It is closely linked to human information processing as it influences reasoning and decision making while directly linking to perception and action implementation (feedback).
Information presentation supports information flow by guiding the operators in a direction.
Please select among the following information interface design requirements to get more information:
- Detectability
- Freedom from Distraction
- Discriminability
- Interpretability
- Conciseness
- Arrangement/ Composition
- Coding
- Colour/ Sound
References
- EN ISO 9241-112 Ergonomics of human-system interaction – Part 112: Principles for the presentation of information. Brussels: CEN
- Kantowitz, B.H., Sorkin, R.D. (1983). Human factors: Understanding people-system relationships. Wiley, New York.
- Wickens, C.D., Hollands, J.G., Banbury, S., Parasuraman, R. (2013). Engineering Psychology and Human Performance. Pearson, Upper Saddle River.
Information Interface Design Requirements – Conciseness
Among the information interface design requirements "Conciseness" is important to allow the operator to perform his/her task.
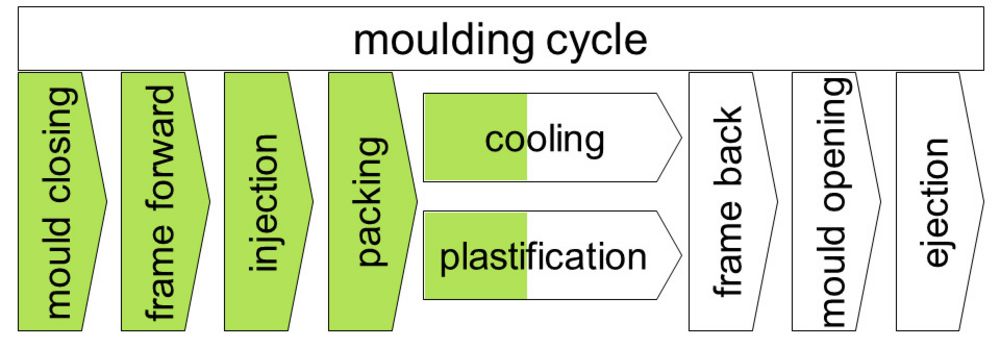
Steps in moulding are supported by gaze flow in horizontal sequence representing the production process within the machine.
Concise information presentation is reduced to presentation of necessary information only and is supported by minimalism, simplicity, task relevance etc.
Figure shows batch procedure of injection moulding machine that guides operators gaze horizontally from start to finish.
References
- EN ISO 9241-112 Ergonomics of human-system interaction – Part 112: Principles for the presentation of information. Brussels: CEN
- Kantowitz, B.H., Sorkin, R.D. (1983). Human factors: Understanding people-system relationships. Wiley, New York.
- Wickens, C.D., Hollands, J.G., Banbury, S., Parasuraman, R. (2013). Engineering Psychology and Human Performance. Pearson, Upper Saddle River.